Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM7HUNW)
| Drug Name |
Testosterone
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AndroGel; Androderm; Androlin; Andronaq; Andropatch; Androsorb; Andrusol; Depotest; Halotensin; Homosteron; Homosterone; Intrinsa; LibiGel; Malerone; Mertestate; Neotestis; Oreton; Orquisteron; Perandren; Primotest; Primoteston; Relibra; Striant; Sustanon; Sustanone; Teslen; Testandrone; Testaqua; Testiculosterone; Testim; Testobase; Testoderm; Testogel; Testolin; Testopropon; Testosteroid; Testosteron; Testosterona; Testosteronum; Testostosterone; Testoviron; Testrone; Testryl; Virormone; Virosterone; Beta testosterone; Cristerona T; Cristerone T; Malogen in Oil; Oreton F; Percutacrine androgenique; Synandrol F; Testoderm Tts; Testopel Pellets; Testosterone and its esters; Testosterone hydrate; Testosterone solution; Testoviron Schering; Testoviron T; Testro AQ; Virilon IM; AA 2500; Andro 100; Andronate 100; Andronate 200; Andropository 200; Andryl 200; CDB 111C; CMC_13449; COL 1621; CP 601B; Everone 200; Sustason 250; Testamone 100; Testred Cypionate 200; Androderm (TN); Androgel (TN); Geno-cristaux gremy; Malestrone (amps); Malogen, aquaspension injection; Neo-Hombreol F; Neo-testis; Oreton-F; Scheinpharm Testone-Cyp; Striant (TN); T-Cypionate; Testim (TN); Testoject-50; Testosterona [INN-Spanish]; Testosterone [Androgenic steroids, anabolic]; Testosterone [INN:BAN]; Testosteronum [INN-Latin]; Trans-Testosterone; Testosterone (JAN/USP); Testrin-P.A; Delta4-Androsten-17beta-ol-3-one; Delta4-androsten-17b-ol-3-one; Androst-4-en-17beta-ol-3-one; Delta(sup 4)-Androsten-17(beta)-ol-3-one; (17beta)-17-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one; (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one; 17-Hydroxy-(17-beta)-androst-4-en-3-one; 17-Hydroxy-(17beta)-androst-4-en-3-one; 17-Hydroxy-4-androsten-3-one; 17-beta-Hydroxy-delta(sup 4)-androsten-3-one; 17-beta-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one; 17b-hydroxy-4-androsten-3-one; 17beta-Hydroxy-3-oxo-4-androstene; 17beta-Hydroxy-4-androsten-3-one; 17beta-Hydroxy-delta(sup4)-androsten-3-one; 17beta-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one; 17beta-Hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3-one; 4-Androsten-17-ol-3-one; 4-Androsten-17beta-ol-3-one; 4-androstene-17beta-ol-3-one; 7-beta-Hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
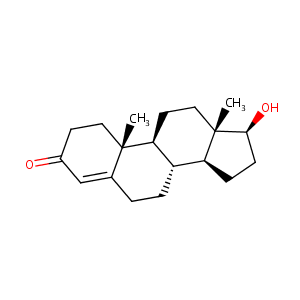 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 288.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Hot flushes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | GA30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Testosterone (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Testosterone FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2858). | ||||
| 3 | ARDANA ANNOUNCES PHASE I RESULTS FOR TESTOSTERONE CREAM. FDAnews report. | ||||
| 4 | Molecular mechanism of androgen action. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1998 Oct 1;9(8):317-24. | ||||
| 5 | FDA Approved Drug Products: Vogelxo Testosterone Gel | ||||
| 6 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 7 | Wang C, Catlin DH, Starcevic B, Leung A, DiStefano E, Lucas G, Hull L, Swerdloff RS: Testosterone metabolic clearance and production rates determined by stable isotope dilution/tandem mass spectrometry in normal men: influence of ethnicity and age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Jun;89(6):2936-41. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-031802. | ||||
| 8 | Ufer M: Comparative pharmacokinetics of vitamin K antagonists: warfarin, phenprocoumon and acenocoumarol. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005;44(12):1227-46. | ||||
| 9 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 10 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 11 | White CM, Ferraro-Borgida MJ, Moyna NM, McGill CC, Ahlberg AW, Thompson PD, Chow MS, Heller GV: The pharmacokinetics of intravenous testosterone in elderly men with coronary artery disease. J Clin Pharmacol. 1998 Sep;38(9):792-7. | ||||
| 12 | Association of the ABCG2 C421A polymorphism with prostate cancer risk and survival. BJU Int. 2008 Dec;102(11):1694-9. | ||||
| 13 | Effect of SLCO1B3 haplotype on testosterone transport and clinical outcome in caucasian patients with androgen-independent prostatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Jun 1;14(11):3312-8. | ||||
| 14 | A novel screening strategy to identify ABCB1 substrates and inhibitors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;379(1):11-26. | ||||
| 15 | Effects of 1alpha,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 and testosterone on miRNA and mRNA expression in LNCaP cells. Mol Cancer. 2011 May 18;10:58. | ||||
| 16 | The exosome-like vesicles derived from androgen exposed-prostate stromal cells promote epithelial cells proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 15;411:115384. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115384. Epub 2020 Dec 25. | ||||
| 17 | Testosterone stimulates adipose tissue 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 expression in a depot-specific manner in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Jul;95(7):3300-8. | ||||
| 18 | 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-3 deficiency: a rare endocrine cause of male-to-female sex reversal. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2006 Sep;22(9):488-94. | ||||
| 19 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 20 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 21 | Asplund K, Wiholm BE, Lithner F "Glibenclamide-associated hypoglycaemia: a report on 57 cases." Diabetologia 24 (1983): 412-7. [PMID: 6411511] | ||||
| 22 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Multaq (dronedarone). sanofi-aventis , Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Synercid (dalfopristin-quinupristin) Rhone-Poulenc Rorer, Collegeville, PA. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Ketek (telithromycin). Aventis Pharmaceuticals, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Tykerb (lapatinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Tukysa (tucatinib). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Emend (aprepitant). Merck & Company Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Serzone (nefazodone). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Trileptal (oxcarbazepine) Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Xcopri (cenobamate). SK Life Science, Inc., Paramus, NJ. | ||||
| 35 | EMEA. European Medicines Agency "EPARs. European Union Public Assessment Reports.". | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Tazverik (tazemetostat). Epizyme, Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 37 | Auclair B, Berning SE, Huitt GA, Peloquin CP "Potential interaction between itraconazole and clarithromycin." Pharmacotherapy 19 (1999): 1439-44. [PMID: 10600094] | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Victrelis (boceprevir). Schering-Plough Corporation, Kenilworth, NJ. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Incivek (telaprevir). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 42 | Barry M, Mulcahy F, Merry C, Gibbons S, Back D "Pharmacokinetics and potential interactions amongst antiretroviral agents used to treat patients with HIV infection." Clin Pharmacokinet 36 (1999): 289-304. [PMID: 10320951] | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Agenerase (amprenavir). Glaxo Wellcome, Research Triangle Pk, NC. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Sustiva (efavirenz). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Fortovase (saquinavir) Roche Laboratories, Nutley, NJ. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Prezista (darunavir). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 49 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Vaprisol (conivaptan). Cumberland Pharmaceuticals Inc, Nashville, TN. | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 53 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 55 | Product Information. Copiktra (duvelisib). Verastem, Inc., Needham, MA. | ||||
| 56 | Product Information. Clolar (clofarabine). sanofi-aventis, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 57 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 58 | Bailey DG, Arnold JMO, Spence JD "Grapefruit juice and drugs - how significant is the interaction." Clin Pharmacokinet 26 (1994): 91-8. [PMID: 8162660] | ||||
| 59 | Product Information. Tasigna (nilotinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 60 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 61 | Doherty MM, Charman WN "The mucosa of the small intestine: how clinically relevant as an organ of drug metabolism?" Clin Pharmacokinet 41 (2002): 235-53. [PMID: 11978143] | ||||
| 62 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 63 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
| 64 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 65 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 66 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 67 | Product Information. Oxbryta (voxelotor). Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc., South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 68 | Kane GC, Lipsky JJ "Drug-grapefruit juice interactions." Mayo Clin Proc 75 (2000): 933-42. [PMID: 10994829] | ||||
| 69 | Product Information. ReVia (naltrexone). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 70 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 71 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
